Curious about lab grown diamonds? Find out everything you need to know about lab diamonds and diamond alternatives.

About Lab Grown Diamonds
The expansion of diamond options available in the market today has led many consumers to wonder, “Are lab diamonds real?” In the simplest sense, lab grown diamonds are diamonds that have been grown in a lab instead of being mined from the earth. They are chemically and optically identical to natural diamonds and are graded with the same scale. The FTC (Federal Trade Commission) recently amended their Jewelry Guides to rule that anything chemically identical to a mined diamond, is in fact, a real diamond. So, laboratory grown diamonds are diamonds – it’s as easy as that.
In order to fully understand what lab grown diamonds are, it’s helpful to know the details of their composition and how they’re made. Before answering the question, “how are lab grown diamonds made?,” it’s important to note that just like naturally mined diamonds from the earth, lab grown diamonds are made of carbon. The diamond industry has traditionally relied on diamonds formed under extreme heat and pressure over millions of years in the earth’s mantle. In a lab, man-made diamonds are formed under those same conditions, only with the help of innovative technology. The result, both mined and lab, is a crystallized carbon structure. This technological advancement has provided consumers with a more sustainable and ethical option while maintaining the same quality and beauty they expect from traditional diamonds.
Another comparison point of lab diamonds vs. real diamonds is quality across a number of optical factors. Similar to mined diamonds, laboratory grown diamonds are graded by IGI (International Gemological Institute) Gemologists on the 4Cs of Diamond Quality: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat Weight. Each stone, lab or mined, will come out completely unique, and the price of a diamond will vary depending on its performance in each of these categories. Furthermore, lab diamonds and natural diamonds can both pass a diamond test, which measures their thermal conductivity and helps confirm their authenticity as genuine diamonds. This tool provides peace of mind for consumers seeking to ensure they are purchasing a genuine diamond, whether it’s lab grown or mined, as reliable testing methods continue to be a critical aspect of the diamond industry.
The Benefits of Lab Grown Diamonds
One of the most significant advantages of lab grown diamonds – and a reason why many consumers choose lab created diamond rings – is their ethical and environmental efficiency.
Unlike mined diamonds, lab created diamonds have minimal environmental impact. It takes considerably less energy to grow diamonds in a lab than it does to mine them from the earth. A one-carat mined diamond costs the planet between 88,000 and 176,000 pounds of displaced earth*. In contrast, each lab grown diamond can save the planet that much alone in displaced earth, plus the energy needed to move it.

Lab diamonds are a less expensive, environmentally and ethically superior choice. With these advantages, there really is no need to buy a mined stone, ever.
About Diamond Alternatives
Diamond alternatives, also known as simulants, are anything that contain similar characteristics, but are chemically different from natural diamonds. They have recently grown in popularity across engagement ring trends, especially since there are many alternatives available in the diamond market, all of which vary in physical and optical features. Some have such similar qualities that it is almost impossible to tell the difference by the naked eye.
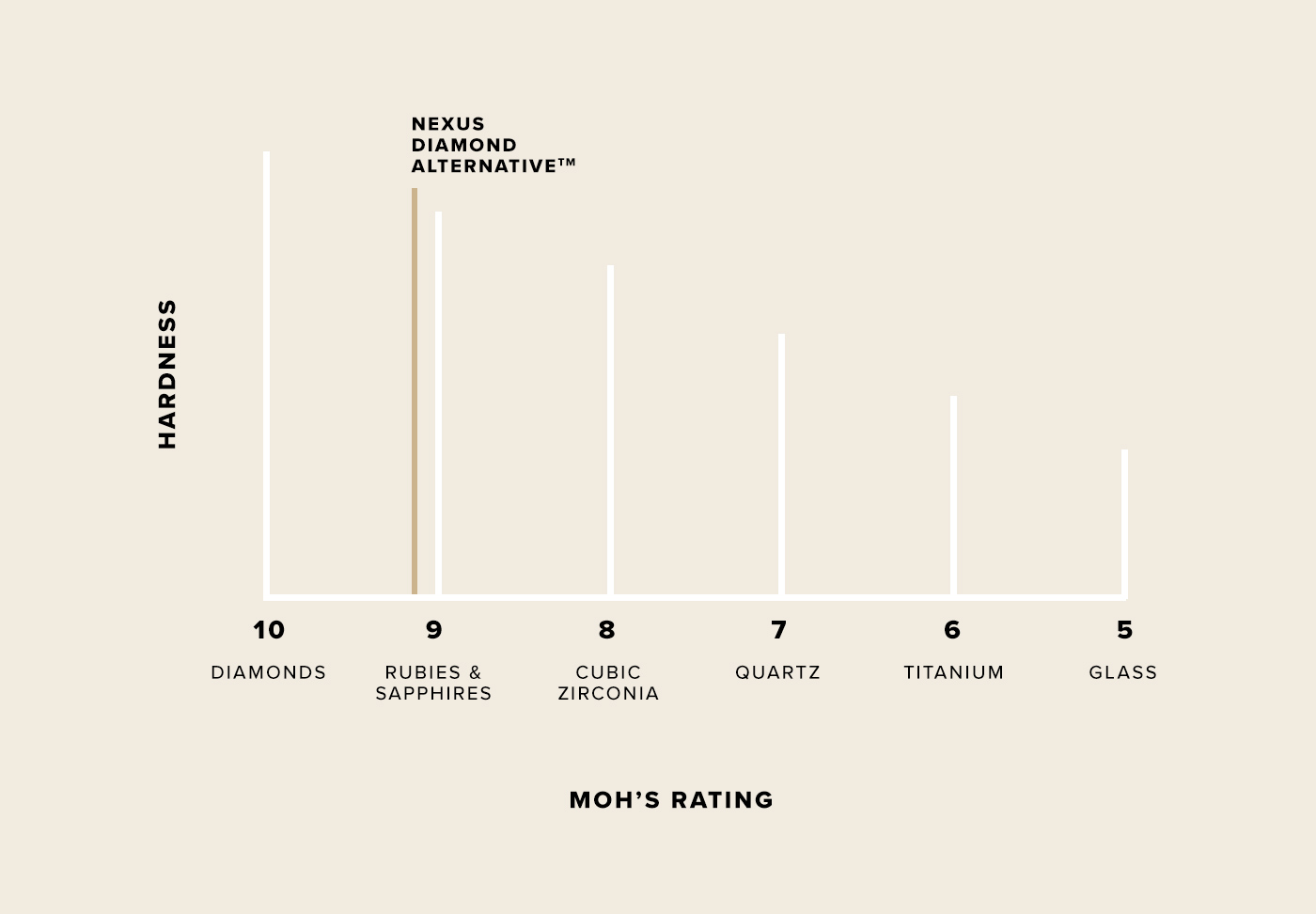
Aside from the chemical composition, another differentiating factor of diamond simulants is how they are measured or qualified. Simulants are not all graded on the same 4Cs scale, like diamonds and lab diamonds are. However, they are all graded based on the same hardness scale. This is called the Mohs scale, which rates stones from softest (1) to hardest (10). The closer a stone is to a perfect rating (10), the more durable and likely it is to last through the everyday wear of a diamond engagement ring or piece of fine jewelry. All diamonds and lab diamonds rate a 10 on the Mohs scale.
The Benefits of Diamond Alternatives
Diamond alternatives feature many of the same benefits as lab diamonds, as they are more cost efficient and environmentally-friendly.
The majority of alternative stones are much less expensive than their mined counterparts (diamonds as well as gemstones). Since each stone is so different, it’s hard to pinpoint an exact range, but some, like Nexus Diamond™ alternatives, may be up to 80% less than mined diamonds. The exact cost comparison will depend on which alternative diamonds or gems you choose and from which company.
Diamond alternatives are not only much less expensive, but they also have great environmental and ethical benefits, similar to lab grown diamonds. Similar to lab diamonds, the production of diamond simulants does not require the displacement of the thousands of pounds of earth needed to find a blood diamond. There is also no chemical runoff from strip mining, which destroys sea habitats for generations. Environmental concerns are almost completely eliminated with alternative stones.

Diamond Alternatives Compared
If you are deciding which stone to purchase, whether when picking an engagement ring or another piece of fine jewelry, weigh your options across the seven most popular diamond alternatives.
THE NEXUS DIAMOND™ ALTERNATIVE
The Nexus Diamond is a simulant stone that most closely resembles the same physical and optical characteristics of a perfect natural diamond. It is IF rated (internally flawless), G color (colorless) and Ideal Cut for maximum brilliance and fire. Moreover, unlike a mined diamond, it is guaranteed to never chip, crack or discolor, making it an heirloom quality stone that will last a lifetime.
The Nexus Diamond is made of a proprietary substrate and patented coating material that results in a heavier, harder and more durable alternative stone. It rates a 9.1 to 9.2 on the Mohs scale. In relation to brilliance, the coating material disperses light at a much closer rate to a natural diamond, resulting in the perfect amount of sparkle.
The Nexus Diamond Is the highest quality alternative stone relative to price. It costs up to 80% less than an earth mined diamond, while keeping all of the qualities that make a perfect diamond so captivating.
CUBIC ZIRCONIA
Cubic zirconia (CZ) is one of the most well-known alternative stones, commonly sold in inexpensive jewelry. However, there is a big difference between cubic zirconia and lab created diamonds or natural diamonds. Although a well-cut CZ may look fairly close to a natural diamond at first, it is very porous, which results in the absorption of contaminants. Eventually, a CZ will become discolored and dull over time.
CZ is made of zirconia dioxide, which disperses light at a much higher rate than a diamond. This is responsible for the “fire” of a stone and will sparkle more than a diamond, sometimes resulting in flashes of rainbow color. It also has a lower refractive, meaning it does not capture light in the same way a diamond does.
Cubic zirconium is softer than a diamond. It rates an 8 on the Mohs scale, which may cause it to chip or crack much more easily. CZ might be a good choice for an inexpensive set of earrings, but will not hold up for the everyday wear of an engagement ring or wedding ring.
MOISSANITE
Moissanite is made of silicon carbide and is also a very common alternative stone used in inexpensive jewelry. Natural moissanite is extremely rare, so most stones of this category that you come in contact with are lab created.
There is a large market for these simulants in jewelry, although their characteristics are far from those of a natural diamond. Due to moissanite’s high amount of brilliance and light dispersion, it produces a “disco ball” like sparkle. This means it is extremely sparkly and commonly reflects rainbow light.
In comparison to CZ, moissanite is a harder stone and much more comparable to a diamond. It rates a 9.2 on the Mohs scale, so it’s less likely to chip or crack during daily wear. When comparing a moissanite vs lab diamond, it’s important to note that it may be durable enough to be set in an engagement ring, but it won’t visually match the look of a true diamond.
MORGANITE
Morganite is made of the mineral beryl, and has an orange or pink tint. It can be found in nature or grown in a lab to have the same chemical and optical properties. Many stones are treated to improve color, which diminishes any orange or brass colors and results in a perfect pink stone.
Morganite has a much lower refractory index than a diamond and even CZ, so light is not captured in the same way. This does not mean it doesn’t reflect sparkle, merely that it will shine light in a different manner.
Although its characteristics are different than a colorless diamond, some brides opt for morganite for a non-traditional center stone or accents. It’s rated a 7.5 to 8 on the Mohs scale, meaning it has about the same durability as a CZ. Due to its low hardness rating and refractory index, morganite is one of the lowest-performing alternative stones.
RUBY
Rubies are made of the mineral corundum, making them a member of the larger corundum family. In a pure form, corundum is colorless, but due to trace elements of chromium, the color can range from light red to dark red. Rubies are also commonly grown in a lab to have the same chemical and physical properties, but without color variation. So unlike their natural form, a lab ruby will turn out a perfect deep red.
Rubies disperse light at a lower rate than diamonds, so they do not sparkle as brilliantly as diamonds. Instead, their deep red color is what makes them stand out.
Rubies rate a 9 on the Mohs scale, so they’re much more durable than other alternative stones, like moissanite. They are an excellent choice for engagement rings or fine jewelry, and can easily perform as an heirloom piece.
SAPPHIRE
Like rubies, sapphires are also part of the corundum family. They are formed naturally, but can also be grown in a lab to have the same chemical, physical and optical properties. Just like rubies, their lab grown form will have no color variation, so they will be the perfect dark blue every time.
Sapphires also do not disperse light at the same rate of diamonds, but are chosen because of their bold and mesmerizing hue. Sapphires are often used as side stones or surrounded by a halo of colorless stones to create balance and add sparkle.
Sapphires rate a 9 on the Mohs scale, so they are great for special pieces needed to last a long time, or handed down for generations. Recently, their unique characteristics have caused them to grow in popularity, and they are now commonly seen in non-traditional engagement rings.
AMETHYST
Amethyst is a purple variety of quartz that also can be found in nature or produced in a gemological lab. Amethyst was used as a gemstone in many ancient cultures and is still frequently used today in birthstone jewelry and cocktail rings. Although they were once a prized, expensive gem, they are now one of the most inexpensive alternative options.
Amethyst is softer than many other alternatives, even CZ, as it rates only a 7 on the Mohs scale. It won’t be the most dependable for long term wear or an heirloom piece like an engagement ring.
The Difference Between Lab Diamonds and Diamond Alternatives
Lab diamonds and diamond alternatives differ in many ways due to their compositional and optical differences. However, since different diamond alternatives vary so greatly, it is difficult to make direct comparisons between alternatives. The main takeaway is that lab diamonds are compositionally the same as mined diamonds and diamond alternatives are not.

No matter what decision you make in the end, either a lab grown diamond or an alternative stone, will be a fiscally and ethically responsible decision. It’s a true win, win, win scenario – a win for the environment, a win for your wallet and a win for you.
Would you buy a lab grown diamond? Tell us in the comments!
*Diamond Nexus strives to provide valuable information, while being clear and honest about products. The Nexus Diamond™ alternative is a patented lab grown stone that, among all simulants, most closely imitates the look, weight and wear of a mined diamond, with two exceptions – it is absolutely perfect in every way, and it costs significantly less. Price points expressed in this blog were taken from popular online retailers and may vary. Learn more about the environmental impact of mining on our blog.